Datasets and catalogs
This page lists the last version for each dataset in Gaia Sky. You can download each dataset directly from within Gaia Sky using the dataset manager (recommended!), or by following the ‘Dataset files’ link in each dataset.
In order to install any of the packages manually, just download it and extract the contents it in your data folder (defaults to $HOME/.local/share/gaiasky/data/ in Linux, and $HOME/.gaiasky/data in Windows and macOS).
Click on the dataset title to reveal more information.
Data packs
Base data pack 🔗
default-data

default-dataRequired data pack.
For Gaia Sky 3.7.2 and above. Contains the solar system planets and moons, minor planets, satellites, orbits, constellations, the Milky Way, grids, locations and other important objects. Without this data pack Gaia Sky won't start.
- Type:
data-pack - Dataset version: v61
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.7.2
- Size: 72.5MiB (76067162)
- Number of objects: 9.92k (9920)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrista@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Credits:
- Gaia Sky development team
- ESA/Gaia/DPAC
- ESA/Planck/C. North
- Visible Earth, Reto Stöckli, NASA Earth Observatory
- U.S. Geological Service
- Stefan Payne-Wardenaar
- Solar System Scope, www.solarsystemscope.com
- Tom Patterson, www.shadedrelief.com
- Phil Stooke, Grant Hutchison
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Texture packs
High resolution textures 🔗
hi-res-textures

hi-res-texturesHigh resolution texture pack including some 4K and 8K textures and cubemaps for planet surfaces and asteroids.
- Type:
texture-pack - Dataset version: v15
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.7.1-2
- Size: 248.1MiB (260203930)
- Number of objects: 76 (76)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Gaia star catalogs
Gaia DR3 best 🔗
gaia-dr3-best

gaia-dr3-bestStar catalog based on Gaia DR3 with only the very best stars in terms of parallax relative error. Contains all stars with up to 0.4%/0.002% bright/faint parallax relative error, and all Hipparcos stars.
- Type:
catalog-gaia - Dataset version: v1
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.6.1
- Size: 43.9MiB (45993709)
- Number of objects: 646.4k (646400)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Gaia DR3 tiny 🔗
gaia-dr3-tiny

Star catalog based on Gaia DR3 with a tiny number of the best bright and faint stars in terms of parallax relative error. Contains all stars with up to 1%/0.01% bright/faint parallax relative error, and all Hipparcos stars.
- Type:
catalog-gaia - Dataset version: v3
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.6.1
- Size: 170.5MiB (178807376)
- Number of objects: 2.55M (2552302)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Gaia DR3 weeny 🔗
gaia-dr3-weeny

Star catalog based on Gaia DR3 with only the very best bright and faint stars in terms of parallax relative error. Contains all stars with up to 0.8%/0.01% bright/faint parallax relative error, and all Hipparcos stars.
- Type:
catalog-gaia - Dataset version: v3
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.6.1
- Size: 129.7MiB (135993182)
- Number of objects: 1.94M (1939279)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Gaia Catalog of Nearby Stars 🔗
catalog-gcns

The Gaia Catalog of Nearby Stars (R.L. Smart et. al., 2020) is a clean and well-characterised catalogue of objects within 100 pc of the Sun from the Gaia Early Data Release 3. The catalogue is estimated to contain at least 92% of stars of stellar type M9 within 100 pc of the Sun.
- Type:
catalog-gaia - Dataset version: v3
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 138.4MiB (145106200)
- Number of objects: 331.08k (331078)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
DR2 White Dwarfs 🔗
catalog-whitedwarfs-dr2

White dwarfs catalog based on GDR2 by Gentile Fusillo et al. 2018, MNRAS 482, 4579 - Brightnesses increased by 10 mag
- Type:
catalog-gaia - Dataset version: v3
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 31.2MiB (32715467)
- Number of objects: 256.08k (256082)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
eDR3 White Dwarfs 🔗
catalog-whitedwarfs-edr3

White dwarfs catalog based on Gaia eDR3 data, by Gentile Fusillo et al. 2021, MNRAS. Contains 359073 high-confidence white dwarf candidates (Pwd>0.75).
- Type:
catalog-gaia - Dataset version: v1
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 31.2MiB (32715468)
- Number of objects: 359.07k (359073)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Gaia DR2 Cepheid and RR Lyrae 🔗
catalog-variablestars-dr2

Chepeid and RR Lyrae stars in Gaia DR2, brightened up by 5 magnitudes.
- Type:
catalog-gaia - Dataset version: v3
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 59.3MiB (62219038)
- Number of objects: 106.34k (106339)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Gaia DR3 Cepheid and RR Lyrae 🔗
catalog-variablestars-dr3

Cepheid and RR Lyrae stars in Gaia DR3, brightened up by 5 magnitudes.
- Type:
catalog-gaia - Dataset version: v1
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 148.8MiB (156012917)
- Number of objects: 186.93k (186928)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
GD-1 stellar stream 🔗
catalog-gd1

GD-1 stream, one of the longest and coldest stellar streams in the Milky Way, with brighter magnitudes for visibility.
- Type:
catalog-gaia - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 109.8KiB (112421)
- Number of objects: 1.36k (1365)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Level-of-detail catalogs
Gaia DR3 default 🔗
gaia-dr3-default
gaia-dr3-defaultStar catalog based on Gaia DR3, with a good balance between good distances and number of stars. Contains all stars with up to 20%/1.5% bright/faint parallax relative error, and all Hipparcos stars.
- Type:
catalog-lod - Dataset version: v3
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.6.1
- Size: 1010.2MiB (1059314876)
- Number of objects: 15.13M (15127025)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Gaia DR3 small 🔗
gaia-dr3-small

Star catalog based on Gaia DR3 with a small number of stars. Contains all stars with up to 10%/0.5% bright/faint parallax relative error, and all Hipparcos stars.
- Type:
catalog-lod - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 534.1MiB (560062416)
- Number of objects: 8.2M (8199560)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Gaia DR3 medium 🔗
gaia-dr3-medium

Star catalog based on Gaia DR3 with a moderate number of stars. Contains all stars with up to 30%/5% bright/faint parallax relative error, and all Hipparcos stars.
- Type:
catalog-lod - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 3.1GiB (3297560681)
- Number of objects: 49.94M (49939229)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Gaia DR3 large 🔗
gaia-dr3-large

Star catalog based on Gaia DR3 with a large number of stars. Contains all stars with up to 50%/12.5% bright/faint parallax relative error, and all Hipparcos stars.
- Type:
catalog-lod - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 7.4GiB (7955471359)
- Number of objects: 122.18M (122183859)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Gaia DR3 very large 🔗
gaia-dr3-verylarge

Star catalog based on Gaia DR3 with a very large number of stars. Contains all stars with up to 50% parallax relative error, and all Hipparcos stars.
- Type:
catalog-lod - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 27.9GiB (29923785876)
- Number of objects: 466.14M (466144211)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Gaia DR3 extra large 🔗
gaia-dr3-extralarge

Star catalog based on Gaia DR3 with an extremely large number of stars. Contains all stars with up to 95% parallax relative error, and all Hipparcos stars.
- Type:
catalog-lod - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 42.1GiB (45256595158)
- Number of objects: 707.16M (707157643)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Gaia DR3 bright 🔗
gaia-dr3-bright

Star catalog based on Gaia DR3 with the brightest stars in the catalog. Contains all stars with up to 90%/1% bright/faint parallax relative error, and all Hipparcos stars.
- Type:
catalog-lod - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 731.0MiB (766497858)
- Number of objects: 11.27M (11269665)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Gaia DR3 RUWE 🔗
gaia-dr3-ruwe

Star catalog based on Gaia DR3. Contains the stars for which the RUWE (re-normalized unit weight error) is <= 1.4, and all Hipparcos stars.
- Type:
catalog-lod - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 57.1GiB (61309496907)
- Number of objects: 957.75M (957749159)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Gaia DR3 bayesian distances 🔗
gaia-dr3-geodist

Star catalog based on Gaia DR3. Contains all stars with bayesian distances as determined by Bailer-Jones et. al., and all Hipparcos stars
- Type:
catalog-lod - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 86.9GiB (93280033261)
- Number of objects: 1.47B (1467764764)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Gaia DR3 fidelity 🔗
gaia-dr3-fidelity

Star catalog based on Gaia DR3. Contains all stars for which the fidelity value is > 0.5, and all Hipparcos stars.
- Type:
catalog-lod - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 23.5GiB (25267306839)
- Number of objects: 393.68M (393678770)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Gaia DR3 photometric distances 🔗
gaia-dr3-photdist

Star catalog based on Gaia DR3. Contains all stars with photometric distances from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra, and all Hipparcos stars.
- Type:
catalog-lod - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 28.1GiB (30156685637)
- Number of objects: 470.81M (470812656)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Star catalogs
Fifth Catalog of Nearby Stars (CNS5) 🔗
catalog-cns5
catalog-cns5The Fifth Catalogue of Nearby Stars (CNS5) aims to provide the most volume-complete sample of stars in the solar neighbourhood. The CNS5 is compiled based on trigonometric parallaxes from Gaia EDR3 and Hipparcos, and supplemented with astrometric data from Spitzer and ground-based surveys carried out in the infrared. The CNS5 catalogue is statistically complete down to 19.7 mag in G-band and 11.8 mag in W1-band absolute magnitudes, corresponding to a spectral type of L8. Continuous updates of observational data for nearby stars from all sources were collected and evaluated. For all known stars in the 25 pc sphere around the Sun, the best values of positions in space, velocities, and magnitudes in different filters are presented.
- Type:
catalog-star - Dataset version: v3
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 1.2MiB (1211990)
- Number of objects: 5.93k (5931)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Hipparcos (new reduction) 🔗
catalog-hipparcos

Hipparcos new reduction (van Leeuwen, 2007) with curated star names, already included in all Gaia catalogs.
- Type:
catalog-star - Dataset version: v6
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.6.8
- Size: 7.7MiB (8094183)
- Number of objects: 117.95k (117955)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Galaxy catalogs
NEARGALCAT 🔗
catalog-nbg

catalog-nbgUpdated Nearby Galaxy Catalog. This table contains an all-sky catalog of 869 nearby galaxies having individual distance estimates within 11 Mpc or corrected radial velocities relative to the Local Group centroid VLG < 600 km s-1. The catalog is a renewed and expanded version of the previous Catalog of Neighboring Galaxies by Karachentsev et al. (2004, AJ, 127, 2031). It collects data on the following galaxy observables: angular diameters, apparent magnitudes in the far-UV, B, and Ks bands, H-alpha and H I fluxes, morphological types, H I-line widths, radial velocities, and distance estimates. In this Local Volume (LV) sample, 108 dwarf galaxies still remain without measured radial velocities. The catalog also lists calculated global galaxy parameters: the linear Holmberg diameters, absolute B magnitudes, surface brightnesses, H I masses, stellar masses estimated via K-band luminosity, H I rotational velocities corrected for galaxy inclination, indicative masses within the Holmberg radius, and three kinds of 'tidal index' which quantify the local density environment. In the reference paper, the authors briefly discuss the Hubble flow within the LV and different scaling relations that characterize galaxy structure and global star formation in them. They also trace the behavior of the mean stellar mass density, H I-mass density, and star formation rate density within the volume considered.
- Type:
catalog-gal - Dataset version: v16
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.6.8-2
- Size: 4.6MiB (4872591)
- Number of objects: 875 (875)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
SDSS DR12 🔗
catalog-sdss-12

Part of Sloan Digital Sky Survey DR12, a catalog of distant, high-redshift galaxies and objects.
- Type:
catalog-gal - Dataset version: v8
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.5.8
- Size: 10.9MiB (11425140)
- Number of objects: 327.83k (327835)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
SDSS DR14 🔗
catalog-sdss-14

Part of Sloan Digital Sky Survey DR14, a catalog of distant, high-redshift galaxies and objects.
- Type:
catalog-gal - Dataset version: v8
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.5.8
- Size: 79.0MiB (82844533)
- Number of objects: 3.04M (3040257)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
SDSS DR17 🔗
catalog-sdss-17

High-redshift galaxies in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey DR17 with comoving distances.
- Type:
catalog-gal - Dataset version: v5
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.5.8
- Size: 69.9MiB (73293039)
- Number of objects: 2.81M (2812409)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
SDSS DR18 🔗
catalog-sdss-18

High-redshift galaxies in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey DR18 with comoving distances.
- Type:
catalog-gal - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.5.8
- Size: 98.3MiB (103124179)
- Number of objects: 3.64M (3637836)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Cluster catalogs
DR3 Open Clusters (Hunt, Reffert) 2023 🔗
catalog-clusters-hunt-reffert-2023
catalog-clusters-hunt-reffert-2023Open cluster catalog produced by Emily Hunt and Sabine Reffert. It contains 2700 open clusters based on Gaia DR3 data. A blind, all-sky search for open clusters using 729 million sources from Gaia DR3 down to magnitude G∼20 was conducted, creating a homogeneous catalogue of clusters including many new objects. For more info refer to the link.
- Type:
catalog-cluster - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.5.0
- Size: 991.7KiB (1015463)
- Number of objects: 7.17k (7167)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Open Clusters DR2 Catalog 🔗
catalog-ocdr2

Open Clusters catalog based on DR2 data, by A. Castro-Ginard et al.
- Type:
catalog-cluster - Dataset version: v7
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.5.0
- Size: 140.5KiB (143890)
- Number of objects: 2.02k (2017)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
MWSC 🔗
catalog-mwsc

Milky Way Star Clusters catalog. Milky Way global survey of star clusters. II. (Kharchenko et. al., 2013).
- Type:
catalog-cluster - Dataset version: v7
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.5.0
- Size: 150.6KiB (154260)
- Number of objects: 3.01k (3006)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Other catalogs
NGC2000 Nebulae 🔗
catalog-nebulae

catalog-nebulaeCatalog of bright emisison or reflection nebulae, planetary nebulae and clusters associated with nebulosity in the NGC2000 catalog. This catalog contains 47 of the most well-known nebulae in the Milky Way. Some of the nebulae are represented as volumes, and some are represented as 3D decals.
- Type:
catalog-other - Dataset version: v9
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.6.5
- Size: 3.0MiB (3197071)
- Number of objects: 47 (47)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Gargantua black hole 🔗
gargantua-blackhole

The black hole from Interstellar, somewhere in the galaxy...
- Type:
catalog-other - Dataset version: v5
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.6.5
- Size: 3.1KiB (3125)
- Number of objects: 1 (1)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Oort cloud 🔗
oort-cloud

Simulated Oort cloud data with 10000 ice particles.
- Type:
catalog-other - Dataset version: v4
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.7.2
- Size: 430.8KiB (441156)
- Number of objects: 10k (10000.0)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrista@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Asteroids and SSO
Asteroids and SSO (Gaia FPR) 🔗
catalog-asteroids-fpr
catalog-asteroids-fprMore than 150k asteroids and other SSO, based on Gaia FPR (Focused Product Release) data. This dataset contains the astrometry of asteroids collected by Gaia over 66 months.
- Type:
catalog-sso - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.7.2
- Size: 14.8MiB (15550964)
- Number of objects: 154.76k (154762)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Asteroids and SSO (Gaia DR3) 🔗
catalog-asteroids-dr3

About 154k asteroids and other SSO, based on Gaia DR3 data.
- Type:
catalog-sso - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 15.3MiB (16080022)
- Number of objects: 154.79k (154787)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
NEA asteroids (Gaia DR3, coloured) 🔗
catalog-asteroids-dr3-nea

Some 390 near Earth asteroids found in the Gaia DR3 catalog.
- Type:
catalog-sso - Dataset version: v1
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 15.3MiB (16080022)
- Number of objects: 154.79k (154787)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Trojan asteroids (Gaia DR3, coloured) 🔗
catalog-asteroids-dr3-trojan

Some 390 near Earth asteroids found in the Gaia DR3 catalog.
- Type:
catalog-sso - Dataset version: v1
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 161.1KiB (164988)
- Number of objects: 1.54k (1545)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Asteroids and SSO (Gaia DR2) 🔗
catalog-asteroids-dr2

Some 14k asteroids and other SSO, based on Gaia DR2 data.
- Type:
catalog-sso - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 908.5KiB (930272)
- Number of objects: 14.1k (14104)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Exoplanets and extrasolar systems
NASA Exoplanet Archive 🔗
nasa-exoplanet-archive
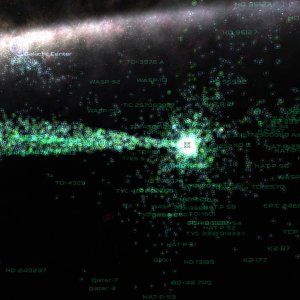
nasa-exoplanet-archiveThe NASA Exoplanet Archive is an astronomical exoplanet catalog and data service that collects and serves public data that support the search for and characterization of extra-solar planets (exoplanets) and their host stars. This dataset contains all planet and host star solutions, regardless of their relationship. This includes atypical systems such as free-floating planets and those with multiple stars. This table also contains Kepler, K2, and TESS candidate solutions for confirmed planet systems, a nearly complete identification of published stellar companions, and projected and true planet obliquities.
The systems in this dataset are shown with glyphs according to the number of planets in the system, and colored accordingly. When approaching a system, the glyph disappears and the actual stars and planets get loaded.
Note that this dataset also includes the stars as defined in the NASA Exoplanet Archive, so if you already have a star catalog you will end up with duplicate objects.
- Type:
system - Dataset version: v1
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.6.3
- Size: 2.9MiB (3078049)
- Number of objects: 9.79k (9793)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Credits:
- This research has made use of the NASA Exoplanet Archive, which is operated by the California Institute of Technology, under contract with the National Aeronautics and Space Administration under the Exoplanet Exploration Program.
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Exonia system 🔗
system-exonia

A made-up partially procedurally generated extra-solar system with two stars, four planets and a moon.
- Type:
system - Dataset version: v4
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.7.1
- Size: 2.4MiB (2556785)
- Number of objects: 7 (7)
- Creator: N/A
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Gl876 system 🔗
system-dr3-gl876

A system with a star and a planet. The Gaia orbit corresponds to the M-dwarf's reflex motion due to the orbiting planet, which is a gas giant. It was one of the earliest radial-velocity discovery. The system is less than 5 pc from the Sun.
- Type:
system - Dataset version: v1
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 1.5KiB (1540)
- Number of objects: 2 (2)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
HD40503 system 🔗
system-dr3-hd40503

A small system with a star and a planet. It is a candidate giant exoplanet around a K dwarf discovered by Gaia astrometry. The orbital period is about 850 days and the inferred planet mass is around 5 Jupiter masses.
- Type:
system - Dataset version: v1
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 1.5KiB (1534)
- Number of objects: 2 (2)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
HD81040 system 🔗
system-dr3-hd81040

A system with a super-Jupiter orbiting a G-type star with a period of 1000 days. The planet was discovered using Gaia radial velocities, and Gaia determined the star's astrometric orbit.
- Type:
system - Dataset version: v1
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 1.5KiB (1517)
- Number of objects: 2 (2)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
HD114762 system 🔗
system-dr3-hd114762

This star hosts the first substellar companion candidate around a solar-type star which was identified from radial velocities in 1989. The Gaia results show that the orbit is seen almost face-on and the companion is, therefore, a low-mass M dwarf.
- Type:
system - Dataset version: v1
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 1.3KiB (1320)
- Number of objects: 2 (2)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
J0805+4812 system 🔗
system-dr3-j0805-4812

This known system is composed of two brown dwarfs orbiting each other with spectral types L4 and T5. Gaia's orbit determination refers to the photocentre of the system, dominated by the brighter primary component.
- Type:
system - Dataset version: v1
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 1.2KiB (1264)
- Number of objects: 2 (2)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
UCAC2 1151977 system 🔗
system-dr3-ucac2-1151977

UCAC2 1151977 is a Sirius-like binary comprising a main sequence primary with a white dwarf companion. The white dwarf is considerably hotter than the primary star.
- Type:
system - Dataset version: v1
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 1.2KiB (1244)
- Number of objects: 2 (2)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
WD0141-675 system 🔗
system-dr3-wd0141-675

A candidate giant exoplanet around a nearby white dwarf discovered by Gaia astrometry. The orbital period is about 33 days and the inferred planet mass is about 9 Jupiter masses. The white dwarf is located within 10 pc from the Sun.
- Type:
system - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.3.1
- Size: 1.5KiB (1522)
- Number of objects: 2 (2)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrsita@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Gaia DR3 black holes 🔗
system-gaia-bhs

This dataset contains the systems of three black holes discovered by Gaia until DR3 (named BH1, BH2, and BH3).
Gaia BH1 is the first dormant black hole candidate. The system contains a slowly rotating G dwarf of 0.92 solar masses orbits around a dark object of 9.62+-0.18 solar masses, which is very likely a BH. The orbital period of the BH is 185.6 days.
Gaia BH2 is in a system with a 1 solar mass red giant plus a dark companion with mass 2.89+-0.3 solar masses, that is very likely a BH. The orbital period of BH2 is 1277 days.
Gaia BH3 is a system which includes the BH3 star and the 33 solar mass dormant black hole. The system sits at about 590 pc (1926 light years) from us, in a halo orbit around the Milky Way. It is the most massive stellar black hole found to date in our Galaxy. The dormant black hole was found in the preliminary Gaia DR4 astrometry. A 0.76+-0.05 solar mass very metal-poor giant plus a dark companion with mass 32.70+-1.46 solar masses, that is very likely a BH. The orbital period is 4253 days. Paper: Discovery of a dormant 33 solar-masses black hole in pre-release Gaia astrometry, Gaia Collaboration, et al., 2024.
- Type:
system - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.6.5
- Size: 145.0KiB (148529)
- Number of objects: 6 (6)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà
- Credits:
- ESA/Gaia/DPAC
- Sources/links:
- Files:
3D iso-density meshes
Dust iso-density maps (Gaia DR2) 🔗
mesh-dust-dr2
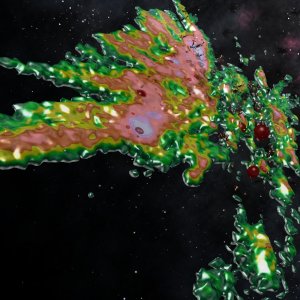
mesh-dust-dr2Dust map iso-density surface map for 15% and 60% density, based on Gaia DR2 data.
- Type:
mesh - Dataset version: v4
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.5.0
- Size: 2.7MiB (2828359)
- Number of objects: 2 (2)
- Creator: Kevin Jardine, Toni Sagristà
- Sources/links:
- Files:
HII regions map (Gaia DR2) 🔗
mesh-hii-dr2

HII regions (clouds of partially ionized gas) based on DR2 data, produced by Kevin Jardine.
- Type:
mesh - Dataset version: v4
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.5.0
- Size: 2.4MiB (2475047)
- Number of objects: N/A (N/A)
- Creator: Kevin Jardine, Toni Sagristà
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Star density map (Gaia DR2) 🔗
mesh-stardensity-dr2

Hot star iso-surface density maps based on Gaia DR2 data. Contains eight iso-density surface maps of hot stars for different preset values
- Type:
mesh - Dataset version: v3
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.5.0
- Size: 80.1MiB (83981902)
- Number of objects: 8 (8)
- Creator: Kevin Jardine, Toni Sagristà
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Dust iso-density maps (Gaia DR3) 🔗
mesh-dust-dr3

30% dust density iso-surface based on DR3 data, produced by Kevin Jardine. Dust from 'Three-dimensional extinction maps: Inverting inter-calibrated extinction catalogues' by J.R. Vergely, R. Lallement and N.L.J. Cox, 2022. Dust extinction cubes provided by Rosine Lallement.
- Type:
mesh - Dataset version: v1
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.6.0
- Size: 1.4MiB (1459180)
- Number of objects: 1 (1)
- Creator: N/A
- Sources/links:
- Files:
HII regions map (Gaia DR3) 🔗
mesh-hii-dr3

HII regions (clouds of partially ionized gas) based on DR3 data, produced by Kevin Jardine. The HII region positions were determined by known ionizing stars and clusters with sizes estimated using Douglas Finkbeiner's H-alpha Full Sky Map and distances taken from 'Estimating Distances from Parallaxes. V. Geometric and Photogeometric Distances to 1.47 Billion Stars in Gaia Early Data Release 3' by C.A.L. Bailer-Jones et.al. 2021.
- Type:
mesh - Dataset version: v1
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.6.0
- Size: 8.9MiB (9336476)
- Number of objects: 1 (1)
- Creator: Kevin Jardine, Toni Sagristà
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Star density map (Gaia DR3) 🔗
mesh-stardensity-dr3

35% star density iso-surfaces based on DR3 data, produced by Kevin Jardine. sosurface algorithm inspired by 'Cosmography of OB stars in the solar neighbourhood.' Astronomy & Astrophysics 584 (2015): A26 by H. Bouy and J. Alves. Hot star density and bar orientation from 'Gaia Data Release 3: Mapping the asymmetric disc of the Milky Way' by the Gaia Collaboration, R. Drimmel, et al. 2022. Data provided by Ronald Drimmel.
- Type:
mesh - Dataset version: v1
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.6.0
- Size: 24.0MiB (25168342)
- Number of objects: 1 (1)
- Creator: Kevin Jardine, Toni Sagristà
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Missions, spacecraft and satellites
ESA Euclid 🔗
spacecraft-euclid

spacecraft-euclidESA Euclid spacecraft, with its orbit and model. Euclid is an ESA mission to map the geometry of the Universe and better understand the mysterious dark matter and dark energy, which make up most of the energy budget of the cosmos. The mission will investigate the distance-redshift relationship and the evolution of cosmic structures by measuring shapes and redshifts of galaxies and clusters of galaxies out to redshifts ~2, or equivalently to a look-back time of 10 billion years. In this way, Euclid will cover the entire period over which dark energy played a significant role in accelerating the expansion of the Universe.
- Type:
spacecraft - Dataset version: v3
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.6.1
- Size: 21.6MiB (22600082)
- Number of objects: N/A (N/A)
- Creator: Kevin Jardine, Toni Sagristà
- Sources/links:
- Files:
James Webb Space Telescope 🔗
spacecraft-jwst

The James Webb Space Telescope, with its orbit around L2 and a wavefront (.obj) 3D model.
- Type:
spacecraft - Dataset version: v4
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.6.1
- Size: 3.4MiB (3540638)
- Number of objects: N/A (N/A)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Hubble Space Telescope 🔗
spacecraft-hst

The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation.
- Type:
spacecraft - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.6.1
- Size: 8.7MiB (9162078)
- Number of objects: N/A (N/A)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà
- Sources/links:
- Files:
International Space Station 🔗
spacecraft-iss

The International Space Station on its low-Earth orbit.
- Type:
spacecraft - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.6.1
- Size: 29.2MiB (30599574)
- Number of objects: N/A (N/A)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà
- Sources/links:
- Files:
GPS Satellite Network 🔗
catalog-gps

Constellation of GPS satellites with their true orbits and locations. The orbital data is pulled on-demand from Celestrak servers in TLE format and updated live. The satellites' 3D models are only an approximation for illustration purposes.
- Type:
spacecraft - Dataset version: v1
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.6.11
- Size: 999.9KiB (1023911)
- Number of objects: 31 (31)
- Creator: Trevor Kjorlien, Plateau Astro
- Credits:
- GPS: USSF
- Dataset: Trevor Kjorlien, Plateau Astro
- 3D model: dh14300 at cgtrader.com, modified by Toni Sagristà
- GPS elements: Celestrak
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Voyagers 1 and 2 🔗
spacecraft-voyagers

NASA's two Voyager spacecraft, which represent the furthest man-made objects go have ever left Earth.
- Type:
spacecraft - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.6.1
- Size: 2.9MiB (3031608)
- Number of objects: N/A (N/A)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Virtual textures
Earth surface VT (Sentinel-2, Blue Marble) 🔗
vt-earth-diffuse-sentinel
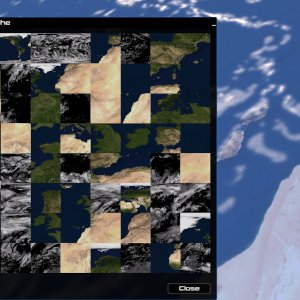
vt-earth-diffuse-sentinelUltra high-resolution (down to 10 m/px) virtual texture for 31 selected urban areas, and 128K elsewhere. Levels 0-5 extracted from NASA's Blue Marble July 86K image. Level 6 and below are processed from Sentinel-2 data. Includes the following urban areas down to 10-20 m/px resolution: Heidelberg, Barcelona, Montreal, New York, Paris, Rome, Berlin, Edinburgh, London, Madrid, Prague, Lisbon, Chicago, San Francisco, Los Angeles, New Delhi, Beijing, Tokyo, Ankara, Budapest, Amsterdam, Cape Town, Kathmandu, Vienna, Bratislava, Mumbai, Cairo, Istanbul, Copenhagen, Cape Canaveral, Andorra la Vella.
- Type:
virtualtex-pack - Dataset version: v0
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.6.10
- Size: 3.4GiB (3659020622)
- Number of objects: 1 (1)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà, tsagrista@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
- Credits:
- Contains modified Copernicus Sentinel-2 data 2023-2025, processed by tsagrista
- Reto Stöckli, NASA Earth Observatory
- Sources/links:
- Files:
128K Earth surface VT (NASA) 🔗
vt-earth-diffuse-nasa

128K Surface virtual texture for the Earth, with 7 global levels and 4 more on the UK. Levels 0-6 extracted from NASA's visible Earth portal, levels 7-10 from Jestr's Celestia dataset.
- Type:
virtualtex-pack - Dataset version: v0
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.4.0
- Size: 1.3GiB (1373115642)
- Number of objects: 1 (1)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà
- Sources/links:
- Files:
128K Earth elevation VT (USGS) 🔗
vt-earth-topography-gmted2010

128K topography virtual texture for the Earth, with 7 global levels. Contains elevation data. Generated from US Geological Survey GMTED2010 dataset.
- Type:
virtualtex-pack - Dataset version: v0
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.4.0
- Size: 645.9MiB (677264527)
- Number of objects: 1 (1)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà
- Sources/links:
- Files:
64K Earth cloud VT (NASA) 🔗
vt-earth-clouds-nasa

64K Earth cloud map as a virtual texture pack. Data from NASA's visible Earth protal, 'Blue Marble: Clouds' dataset.
- Type:
virtualtex-pack - Dataset version: v0
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.4.0
- Size: 378.3MiB (396667328)
- Number of objects: 1 (1)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà
- Sources/links:
- Files:
64K Mars diffuse VT (Celestia) 🔗
vt-mars-diffuse-vanvliet

64K Mars surface virtual texture pack. From Celestia moderlothe, made by John Van Vliet.
- Type:
virtualtex-pack - Dataset version: v0
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.4.0
- Size: 1.2GiB (1340485779)
- Number of objects: 1 (1)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà
- Sources/links:
- Files:
64K Mars elevation VT (MOLA/USGS) 🔗
vt-mars-topography-mola

64K Mars topography virtual texture, with 6 global levels. Contains elevation data. Generated from USGS Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA), an instrument on the Mars Global Surveyor (MSG).
- Type:
virtualtex-pack - Dataset version: v0
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.4.0
- Size: 67.7MiB (71003938)
- Number of objects: 1 (1)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà
- Sources/links:
- Files:
64K Moon diffuse VT (Celestia) 🔗
vt-moon-diffuse-vanvliet

64K surface virtual texture pack for the Moon (LRO WAC). From Celestia moderlothe, made by John Van Vliet.
- Type:
virtualtex-pack - Dataset version: v0
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.4.0
- Size: 2.7GiB (2938258080)
- Number of objects: 1 (1)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà
- Sources/links:
- Files:
8K Moon topography VT (LRO WAC DTM) 🔗
vt-moon-topography-lro

8K Moon topography virtual texture (LRO WAC DTM). The WAC Digital Terrain Model was derived from WAC observations, and covers 98.2% of the lunar surface. Using digital photogrammetric techniques, the GLD100 was computed from 69,000 WAC stereo models. Due to persistent shadows near the poles it is not possible to create a complete WAC stereo map at the very highest latitudes.
- Type:
virtualtex-pack - Dataset version: v0
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.4.0
- Size: 8.4MiB (8802327)
- Number of objects: 1 (1)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà
- Sources/links:
- Files:
32K Moon topography NASA (SVS, DEM LRO:LOLA) 🔗
vt-moon-topography-nasa

32K Moon topography virtual texture (NASA Scientific Visualization Studio, dataset: DEM LRO:LOLA). he displacement map (also known as a height map or elevation map) was taken directly from the latest (as of spring 2019) gridded data products of the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter instrument team. LOLA data is archived on the Geosciences Node of the Planetary Data System. A small subset of the LOLA data stored there, the global cylindrical projections at 4, 16, and 64 pixels per degree, has been reformatted here as uncompressed TIFF files, in vertical units of either floating-point kilometers or 16-bit unsigned integer half-meters.
The reference surface for all LRO data is a sphere of radius 1737.4 km. LOLA's gridded elevation data is published as signed 16-bit integers in units of half-meters relative to this radius. For the floating-point TIFFs, the source data was divided by 2000. For the unsigned 16-bit TIFFs, the source data was offset by +20,000 (10 km) so that all of the values are positive. This latter format is provided for software that doesn't work well with either floating-point or signed integer files. Credits: Ernie Wright (USRA), Noah Petro (NASA/GSFC).
- Type:
virtualtex-pack - Dataset version: v1
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.4.0
- Size: 41.1MiB (43124453)
- Number of objects: 1 (1)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà
- Sources/links:
- Files:
Volumetric objects and effects
Volumetric Aurora 🔗
volumetric-aurora

volumetric-auroraA volumetric aurora borealis and australis for the Earth. This is based on the paper by Lawlor et al. The aurora is rendered using a ray-marching algorithm, producing a volumetric object.
- Type:
volume - Dataset version: v2
- Minimum Gaia Sky version: 3.6.5
- Size: 46.9KiB (48046)
- Number of objects: 1 (1)
- Creator: Toni Sagristà
- Sources/links:
- Files: